The Ultimate Guide to Fiber Cement Siding: Pros and Cons explores the multifaceted world of this increasingly popular exterior cladding. We’ll delve into its rich history, examine its remarkable durability and low-maintenance qualities, and weigh its considerable advantages against potential drawbacks. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision about whether fiber cement siding is the right choice for your next project.
From understanding its composition and installation process to assessing its long-term cost-effectiveness and environmental impact, we’ll cover all the essential aspects. We’ll also compare fiber cement to other siding materials, helping you navigate the complexities of choosing the best option for your specific needs and budget.
Introduction to Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is a popular exterior cladding material known for its durability and low maintenance requirements. It’s a composite material made from a mixture of cement, cellulose fibers (often wood pulp), and other additives such as sand and silica. This blend creates a strong, stable panel that resists damage from the elements.
Fiber cement siding’s journey in the building industry began in the late 19th century, with early iterations exhibiting limitations in terms of workability and aesthetics. However, significant advancements in manufacturing processes throughout the 20th century led to the development of more durable, versatile, and aesthetically pleasing products. Modern fiber cement siding offers a wide array of colors, textures, and styles, mimicking the look of wood, stone, or stucco while offering superior performance. The material’s increased popularity stems from its ability to effectively address many of the drawbacks associated with traditional siding materials.
Composition and Manufacturing of Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is produced through a precise manufacturing process. A slurry of cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives is mixed and formed into panels. These panels are then cured under controlled conditions to achieve the desired strength and durability. The final product undergoes a finishing process, which may include painting or texturing, to enhance its aesthetic appeal and provide added protection against the elements. Different manufacturers may employ slight variations in their processes and formulations, resulting in some differences in the final product’s properties. However, the core components and manufacturing principles remain consistent across the industry.
Advantages of Fiber Cement Siding
The popularity of fiber cement siding is largely due to its numerous advantages. It offers exceptional durability, resisting damage from impact, moisture, and insects. Unlike wood, it won’t rot or be susceptible to termite infestations. Its inherent fire resistance is another significant benefit, providing an extra layer of safety for homes. Furthermore, fiber cement siding requires minimal maintenance, saving homeowners time and money in the long run. Its longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to its cost-effectiveness over its lifespan. Finally, the wide variety of styles and colors available allows for significant aesthetic flexibility, accommodating diverse architectural preferences.
Pros of Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding offers a compelling combination of durability, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for homeowners seeking a long-lasting and low-maintenance exterior. Its superior performance compared to other siding materials translates to significant advantages over the building’s lifespan.
Durability and Longevity
Fiber cement siding boasts exceptional durability and longevity, significantly outlasting many alternative materials. Its composition—a blend of cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives—creates a remarkably strong and resilient product resistant to impact, rot, insect infestation, and extreme weather conditions. Unlike wood, which is susceptible to warping, rotting, and insect damage, or vinyl, which can become brittle and crack under harsh sunlight, fiber cement maintains its structural integrity for decades. This inherent strength reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, resulting in long-term cost savings. For example, a home sided with fiber cement in a coastal region, known for its harsh weather, would require far less maintenance and replacement than a home with wood siding in the same location.
Fire Resistance
Fiber cement siding possesses inherent fire-resistant properties, offering a significant safety advantage over combustible materials like wood. Its non-combustible nature helps to slow the spread of flames and protect the home’s structure in the event of a fire. This fire resistance is often rated by independent testing agencies, providing homeowners with quantifiable assurance of safety. In areas with strict fire codes or high wildfire risk, fiber cement siding’s fire-resistant qualities are a crucial factor in choosing exterior cladding. The added safety provided contributes to peace of mind for homeowners and potentially lower insurance premiums.
Low Maintenance and Cost Savings
Fiber cement siding requires minimal maintenance, contributing to substantial long-term cost savings. Unlike wood siding, which needs regular painting and sealing to prevent rot and insect damage, or vinyl siding, which can fade and crack over time, fiber cement typically only requires occasional cleaning. This low-maintenance nature translates into reduced labor costs and material expenses associated with repairs and repainting. The initial investment in fiber cement siding is often higher than other options, but the long-term savings in maintenance and replacement far outweigh this initial cost, making it a financially sound choice over the building’s lifetime. Consider a 50-year timeframe; the cumulative cost of maintaining wood or vinyl siding could easily exceed the initial cost difference.
Lifespan Comparison Table
The table below compares the lifespan, maintenance costs, and fire resistance of fiber cement siding with other common siding materials. Note that the figures provided are estimates based on industry averages and can vary depending on factors like climate and maintenance practices.
| Material | Lifespan (Years) | Maintenance Cost (Estimate) | Fire Resistance Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Low | Non-combustible |
| Wood | 15-30 | Medium-High | Combustible |
| Vinyl | 20-30 | Medium | Combustible |
| Aluminum | 30-40 | Low-Medium | Non-combustible |
Cons of Fiber Cement Siding
While fiber cement siding offers numerous advantages, it’s crucial to acknowledge its potential drawbacks. Understanding these limitations will help homeowners make informed decisions about whether this material is the right choice for their project. This section will explore the key disadvantages associated with fiber cement siding, focusing on cost, installation challenges, susceptibility to damage, and weight considerations.
High Initial Cost
Fiber cement siding is significantly more expensive than many alternative siding materials, such as vinyl or aluminum. The higher cost is attributed to the premium materials used in its manufacture and the more complex installation process. For example, a homeowner might expect to pay double or even triple the price per square foot compared to vinyl siding. This increased upfront investment needs to be carefully weighed against the long-term benefits, such as durability and longevity. Budgeting for this higher initial cost is essential for any project planning.
Installation Complexity and Labor Costs
Installing fiber cement siding requires specialized skills and tools. Unlike simpler materials, it necessitates precise cutting and handling to avoid damage. The weight of the material also presents challenges, demanding experienced installers capable of safely and efficiently handling the panels. This skilled labor translates to higher installation costs, potentially adding substantially to the overall project expense. A lack of experienced installers in a particular area can further drive up costs and lead to project delays.
Susceptibility to Impact Damage and Cracking
Despite its durability, fiber cement siding is susceptible to cracking from impacts, such as those from falling branches or accidental damage during construction. While it is more resistant to dents and scratches than some materials, significant impacts can cause fractures, requiring repairs or panel replacements. These repairs can be costly and time-consuming, especially if extensive damage occurs. The use of protective measures during construction and landscaping can help minimize the risk of such damage.
Weight and Installation Implications
Fiber cement siding is considerably heavier than vinyl or aluminum siding. This increased weight impacts the installation process, requiring stronger scaffolding and more robust support structures. It also increases the physical demands on installers, potentially slowing down the installation process and increasing labor costs. For older homes with weaker structural components, the added weight might necessitate additional structural reinforcement before installation, further increasing the project’s complexity and cost. This weight consideration is a significant factor to consider, particularly for larger projects or homes with existing structural limitations.
Types and Styles of Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding offers a wide variety of options to suit diverse architectural styles and homeowner preferences. The choice extends beyond simply choosing a color; the type of siding and its finish significantly impact the overall aesthetic and longevity of your home’s exterior. Understanding these choices is crucial for making an informed decision.
Fiber cement siding comes in several primary forms, each offering unique advantages and visual characteristics. The selection process often involves considering factors such as the home’s style, the desired level of maintenance, and the overall budget.
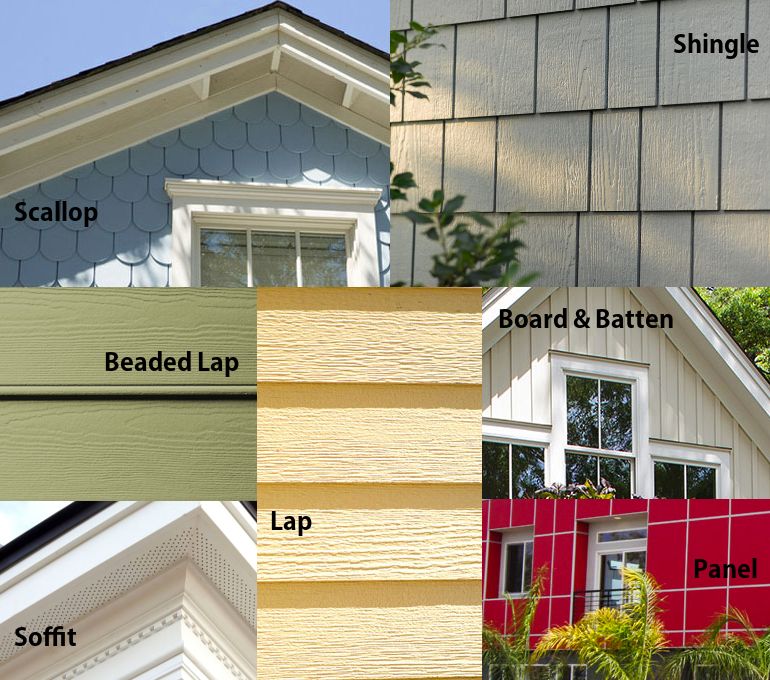
Fiber Cement Siding Types
Fiber cement siding is primarily available in three main types: panels, shingles, and shakes. Panels are the most common, offering large, flat surfaces for easy installation and a clean, modern look. Shingles and shakes, on the other hand, mimic the appearance of traditional wood roofing materials, providing a more textured and rustic aesthetic. The choice depends heavily on the desired visual effect.
Fiber Cement Siding Styles and Finishes
The style and finish of fiber cement siding contribute significantly to its overall appeal. Manufacturers offer a range of profiles and textures designed to complement various architectural styles, from contemporary to traditional. Finishes range from smooth to deeply textured, offering options to emulate wood grain, stone, or even stucco. These finishes not only impact the visual appearance but also influence the siding’s ability to withstand weathering and maintain its color over time. Careful consideration of these factors ensures a visually pleasing and durable exterior.
Examples of Fiber Cement Siding Textures and Colors
The availability of textures and colors in fiber cement siding is extensive, allowing for a high degree of customization. This allows homeowners to seamlessly integrate the siding with their existing landscape and architectural design.
- Textures: Smooth, wood grain (vertical or horizontal), stucco, clapboard, and rough-hewn.
- Colors: A vast spectrum is available, including earth tones like beige, brown, and gray; brighter colors such as red, blue, and green; and even custom color-matching options to perfectly complement a home’s design. Examples include classic white, deep charcoal gray, warm earth tones like terracotta, and vibrant shades of blue or green to suit a variety of styles.
Installation Process of Fiber Cement Siding
Installing fiber cement siding is a complex process best left to experienced professionals. However, understanding the general steps involved can help homeowners effectively communicate with contractors and oversee the project. Proper installation ensures the longevity and performance of the siding, protecting your home from the elements and enhancing its curb appeal.
The installation process typically begins with careful preparation and planning, followed by the installation of the siding itself, and finally, finishing touches to complete the project. Each step requires precision and attention to detail to achieve a professional-looking and durable finish.
Necessary Tools and Equipment
Proper tools are essential for a successful fiber cement siding installation. Using the correct tools ensures efficiency and prevents damage to the siding material. Improper tools can lead to delays, costly repairs, or even injuries.
A comprehensive tool kit might include: measuring tapes, levels, chalk lines, circular saws with appropriate blades for fiber cement, jigsaws, drills with various drill bits, nail guns (with appropriate nails), safety glasses, work gloves, ladders, scaffolding (if needed), and a variety of fasteners specifically designed for fiber cement siding.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
The installation process generally follows a sequence of steps, although specific details may vary depending on the siding type and house design. Adhering to the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial for warranty purposes and optimal performance.
- Preparation: This involves thoroughly inspecting the existing wall sheathing, ensuring it is sound and free from damage. Any necessary repairs, such as replacing rotten wood or leveling uneven surfaces, should be completed before siding installation begins. This stage also includes installing any necessary house wrap or moisture barrier.
- Framing and Furring: Depending on the project, furring strips may be required to create a level surface for the siding. This is especially important on older homes with uneven walls. Proper framing ensures consistent spacing and a professional finish.
- Siding Installation: Starting at a corner or a designated point, installers typically begin fastening the siding panels to the wall using appropriate nails or screws. Precise measurements and careful alignment are critical to maintain straight lines and consistent spacing between panels. Overlapping panels are crucial for weatherproofing.
- Cutting and Fitting: Fiber cement siding often requires cutting to fit around windows, doors, and corners. Precise cuts are essential for a clean and professional look. Using appropriate cutting tools and techniques minimizes dust and ensures clean, accurate cuts.
- Caulking and Sealing: After installation, all gaps and seams should be carefully caulked and sealed to prevent water penetration. High-quality caulking materials are essential for long-term protection. This step is critical for preventing water damage and ensuring the siding’s longevity.
- Finishing Touches: This includes installing trim, flashing, and other accessories to complete the project. Careful attention to detail ensures a professional and aesthetically pleasing finish.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
Fiber cement siding installation involves working at heights and using power tools, so safety is paramount. Failure to follow safety procedures can lead to serious injury.
Essential safety measures include: always wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, dust masks, and gloves; using appropriate safety harnesses and fall protection when working at heights; ensuring proper ventilation when using power tools; following all manufacturer’s instructions for tools and materials; and maintaining a clean and organized worksite.
Maintenance and Repair of Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding, while durable, requires regular maintenance to preserve its beauty and longevity. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature deterioration and costly repairs. A proactive approach, involving routine cleaning and prompt attention to minor damage, significantly extends the lifespan of your siding.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Regular cleaning is crucial for preventing dirt, mildew, and algae buildup. This buildup not only detracts from the siding’s appearance but can also compromise its structural integrity over time. A yearly cleaning, using a pressure washer set to a low pressure setting and a solution of mild detergent and water, is recommended. Always test the cleaning solution in an inconspicuous area first to ensure it doesn’t damage the siding’s finish. For stubborn stains, a solution of bleach and water (always following the manufacturer’s instructions for dilution) may be necessary, but caution should be exercised to avoid damaging the surface. After cleaning, rinse thoroughly with clean water. Inspect the siding for any signs of damage after cleaning, addressing any issues promptly.
Addressing Common Issues
Several issues can arise with fiber cement siding over time. Cracks, chips, and holes are common, often caused by impacts from debris or weather events. These should be addressed promptly to prevent water damage and further deterioration. Mildew and algae growth can also occur, particularly in shaded or humid areas. Regular cleaning, as previously described, helps prevent this. Paint fading is another potential issue, especially with darker colors. Repainting may be necessary every 5-10 years, depending on the climate and the quality of the paint used. Loose or damaged caulking around windows and doors should also be addressed immediately to prevent water intrusion.
Cleaning and Repairing Minor Damages
Cleaning minor stains and addressing small damages can often be handled with DIY methods. For cleaning, a stiff brush and a solution of mild detergent and water are often sufficient. For minor chips or cracks, a high-quality exterior-grade caulk that matches the siding’s color can be used to fill the gaps. Allow the caulk to dry completely before painting to match the surrounding area. For larger holes or more significant damage, it’s advisable to consult a professional siding contractor. They have the expertise and tools to properly repair the damage and ensure the longevity of your siding. Using inappropriate repair materials or techniques can compromise the siding’s integrity and potentially lead to more extensive and costly repairs in the future. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for cleaning and repair procedures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fiber cement siding, while offering numerous advantages in terms of durability and aesthetics, also carries an environmental footprint that needs careful consideration. Understanding the life cycle of this material, from manufacturing to disposal, is crucial for evaluating its overall sustainability. This section will examine the environmental impact of fiber cement siding, comparing it to alternatives and exploring its recyclability and sustainable sourcing practices.
The manufacturing process of fiber cement siding involves several steps that contribute to its environmental impact. Cement production, a key component, is energy-intensive and releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas. The extraction and processing of the other raw materials – cellulose fibers and sand – also consume energy and resources. Transportation of these materials and the finished product adds to the overall carbon footprint. Disposal of fiber cement siding, while not necessarily posing a significant immediate environmental hazard, does contribute to landfill waste. However, the durability of fiber cement siding means that it typically lasts for decades, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste generation compared to shorter-lived materials.
Manufacturing and Disposal Impacts
Fiber cement siding’s manufacturing process contributes to greenhouse gas emissions primarily through cement production. The high energy demand for kiln firing and the chemical reactions involved in cement hydration release considerable CO2. The extraction of raw materials also necessitates energy consumption and can lead to habitat disruption or water pollution depending on extraction methods and location. At the end of its lifespan, the disposal of fiber cement siding contributes to landfill volume. While the material itself is generally inert and non-toxic, the sheer volume of discarded siding contributes to land usage concerns. Some regions are exploring options for recycling or repurposing fiber cement waste, but these practices are not yet widespread. The overall environmental impact is therefore a complex issue dependent on factors such as manufacturing processes, transportation distances, and end-of-life management strategies.
Comparison to Other Siding Materials
Compared to other common siding materials, fiber cement’s environmental profile presents a mixed picture. Vinyl siding, for example, is derived from petroleum, a non-renewable resource, and its production generates greenhouse gases. However, vinyl siding is often lighter and easier to transport, potentially reducing transportation emissions. Wood siding, while a renewable resource, often requires the harvesting of trees, potentially leading to deforestation and habitat loss if not sourced sustainably. The manufacturing and transportation of metal siding, often made from steel or aluminum, involve significant energy consumption and resource extraction. The relative environmental impact of each material depends on factors such as the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, transportation distances, and end-of-life management. Life cycle assessments are often used to compare the overall environmental impact of these different materials. For instance, studies may consider the energy used in production, the emissions released, and the impact on water and land resources throughout the entire life cycle of each siding material.
Recyclability and Sustainable Sourcing
The recyclability of fiber cement siding is currently limited. While the components themselves (cement, cellulose fibers, and sand) are naturally occurring materials, separating and reprocessing them from the composite is challenging and not economically viable on a large scale in many areas. However, research and development efforts are exploring methods to improve the recyclability of fiber cement, potentially focusing on the recovery and reuse of cement or the incorporation of recycled content in the manufacturing process. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials is also a crucial aspect. Using recycled cement content in the manufacturing process can reduce the overall environmental impact. Sourcing cellulose fibers from sustainably managed forests ensures that the material is not contributing to deforestation. Furthermore, responsible sand mining practices can help to minimize the environmental damage associated with sand extraction. The future of fiber cement siding’s sustainability hinges on advancements in recycling technologies and a greater emphasis on sustainable sourcing practices throughout its supply chain.
Cost Considerations for Fiber Cement Siding
Choosing the right siding for your home involves careful consideration of various factors, and cost is undoubtedly a significant one. Fiber cement siding, while offering numerous advantages in terms of durability and longevity, comes with a price tag that needs careful evaluation. This section will break down the costs associated with fiber cement siding, allowing you to make an informed decision based on your budget and long-term goals.
Fiber cement siding’s cost is influenced by several key elements: material selection (including thickness and texture), labor costs (highly variable based on location and project complexity), and the overall size of the project. Additionally, the need for repairs and maintenance over the siding’s lifespan also factors into the total cost of ownership. Understanding these components allows for a realistic budget projection and informed comparison with other siding options.
Breakdown of Costs
The total cost of fiber cement siding is comprised of material costs, installation costs, and potential maintenance and repair costs over the lifetime of the siding. Material costs vary depending on the manufacturer, thickness, texture, and color choices. Higher-end options with intricate textures and colors will naturally command higher prices. Installation costs are significantly influenced by factors such as the complexity of the house’s design (e.g., numerous dormers or intricate trim work), the size of the house, and the prevailing labor rates in your region. Finally, while fiber cement is durable, occasional repairs may be needed due to damage from severe weather or accidental impact. These costs are typically minor compared to the initial investment but should be factored into the overall cost equation.
Comparison to Other Siding Options
To understand the value proposition of fiber cement siding, it’s essential to compare its total cost of ownership with other common siding materials like vinyl, wood, and aluminum. While vinyl siding often boasts a lower initial cost, its shorter lifespan and susceptibility to damage can lead to higher long-term expenses. Wood siding, though aesthetically pleasing, requires significant and ongoing maintenance, including painting or staining, making its overall cost potentially higher than fiber cement over the long run. Aluminum siding, while relatively low-maintenance, is less durable than fiber cement and can be prone to dents and damage.
Cost Comparison Table
The following table provides a general comparison of the costs associated with different siding materials. It’s crucial to remember that these are estimates, and actual costs will vary significantly based on location, project specifics, and material choices.
| Material | Initial Cost (per sq ft) | Installation Cost (per sq ft) | Estimated Lifetime Cost (per sq ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Cement | $3 – $8 | $3 – $7 | $6 – $15 |
| Vinyl | $1 – $3 | $1 – $3 | $4 – $6 |
| Wood | $2 – $6 | $3 – $7 | $8 – $15 |
| Aluminum | $2 – $4 | $2 – $4 | $4 – $8 |
*Note: These figures are rough estimates and can vary significantly based on location, project complexity, and material choices. It’s always recommended to obtain multiple quotes from reputable contractors for an accurate cost assessment for your specific project.*
Choosing the Right Fiber Cement Siding
Selecting the ideal fiber cement siding involves careful consideration of several key factors to ensure both aesthetic appeal and long-term durability. The right choice depends on your home’s architectural style, climate, budget, and personal preferences. Making informed decisions in these areas will contribute to a successful project and a beautiful, lasting exterior.
Choosing the appropriate fiber cement siding requires a holistic approach, balancing aesthetic considerations with practical factors. This includes evaluating the home’s architectural style, the local climate, and the overall budget. Understanding the nuances of color, style, and thickness selection is crucial, as is selecting a qualified and reputable installer.
Color Selection for Fiber Cement Siding
The color of your fiber cement siding significantly impacts your home’s curb appeal and overall aesthetic. Fiber cement siding is available in a wide range of colors, from classic neutrals to bold and vibrant hues. Consider your home’s architectural style, the surrounding landscape, and your personal preferences when making your selection. Lighter colors tend to reflect more sunlight, potentially reducing cooling costs in warmer climates, while darker colors can absorb more heat. Durable pigments are crucial for long-term color retention, preventing fading and discoloration over time. It’s advisable to examine samples in different lighting conditions to ensure the color suits your needs. For example, a deep navy might look stunning in bright sunlight but appear much darker in the shade.
Style and Texture Considerations for Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding comes in various styles and textures to complement diverse architectural styles. Options range from smooth, contemporary looks to rustic, wood-like textures. Consider the architectural style of your home and choose a siding style that complements it. For instance, a traditional home might benefit from clapboard siding with a wood-grain texture, while a modern home might look best with smooth, horizontal panels. The texture of the siding also plays a role in its visual appeal and maintenance requirements. Textured siding can better conceal minor imperfections, while smooth siding provides a clean, sleek look. Examining samples of different styles and textures in various lighting conditions can aid in making an informed decision.
Thickness and Durability of Fiber Cement Siding
The thickness of fiber cement siding directly impacts its durability and resistance to damage. Thicker panels are generally more robust and better able to withstand impacts and extreme weather conditions. While thicker panels often mean a higher initial cost, the increased longevity and reduced risk of damage can offset this expense in the long run. Consider the climate in your area; regions with frequent strong winds or hailstorms might benefit from thicker panels. For example, a coastal region might warrant thicker siding to better withstand wind and salt spray. Consulting building codes and local weather patterns can provide guidance on the appropriate thickness for your specific location.
Selecting a Reputable Fiber Cement Siding Installer
Choosing a skilled and reputable installer is paramount to ensuring a successful fiber cement siding installation. A qualified installer will possess the necessary expertise to properly prepare the surface, install the siding correctly, and address any potential issues. Check references, verify licensing and insurance, and seek recommendations from friends, family, or other professionals. A reputable installer will provide a detailed estimate, adhere to safety standards, and offer a warranty on their workmanship. It’s crucial to ensure the installer has experience with fiber cement siding specifically, as its installation differs from other siding materials. Confirming the installer’s adherence to manufacturer’s guidelines is also important for ensuring the longevity of the siding.
Final Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the decision of whether to use fiber cement siding hinges on a careful consideration of your individual priorities and circumstances. While its superior durability, fire resistance, and longevity offer significant advantages, factors like initial cost and installation complexity must be weighed. By understanding both the pros and cons outlined in this guide, you can confidently determine if fiber cement siding is the ideal solution to enhance the beauty, safety, and value of your property for years to come.